 Now, consider a flat plate composed of two materials, steel on the left side and iron on the right, then they are welded together in the middle with copper. The dimensions of the plate are 1×1×0.2m, with the cross-sectional area as shown in the following figure,
Now, consider a flat plate composed of two materials, steel on the left side and iron on the right, then they are welded together in the middle with copper. The dimensions of the plate are 1×1×0.2m, with the cross-sectional area as shown in the following figure,
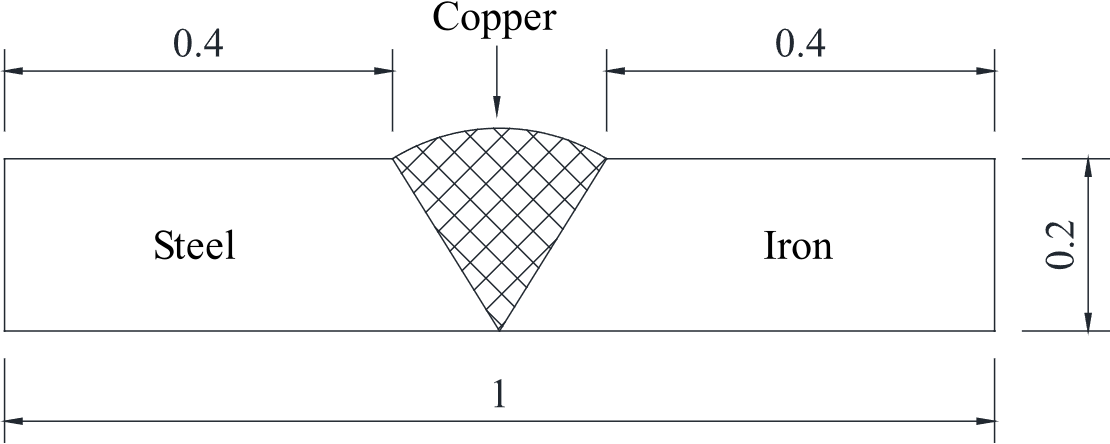
After welding, the initial temperature of the plate is 800°C. The plate is placed in air at a temperature of 30°C, with a convection coefficient of 110W/(m^2·°C). Analyze the temperature field and stress field after 10 minutes.
The material properties are as shown in the following table (Click to DOWNLOAD the table):
For this type of thermal analysis, this article selects PLANE13 and SOLID5 thermal-stress coupling elements. The steel material settings are as follows,
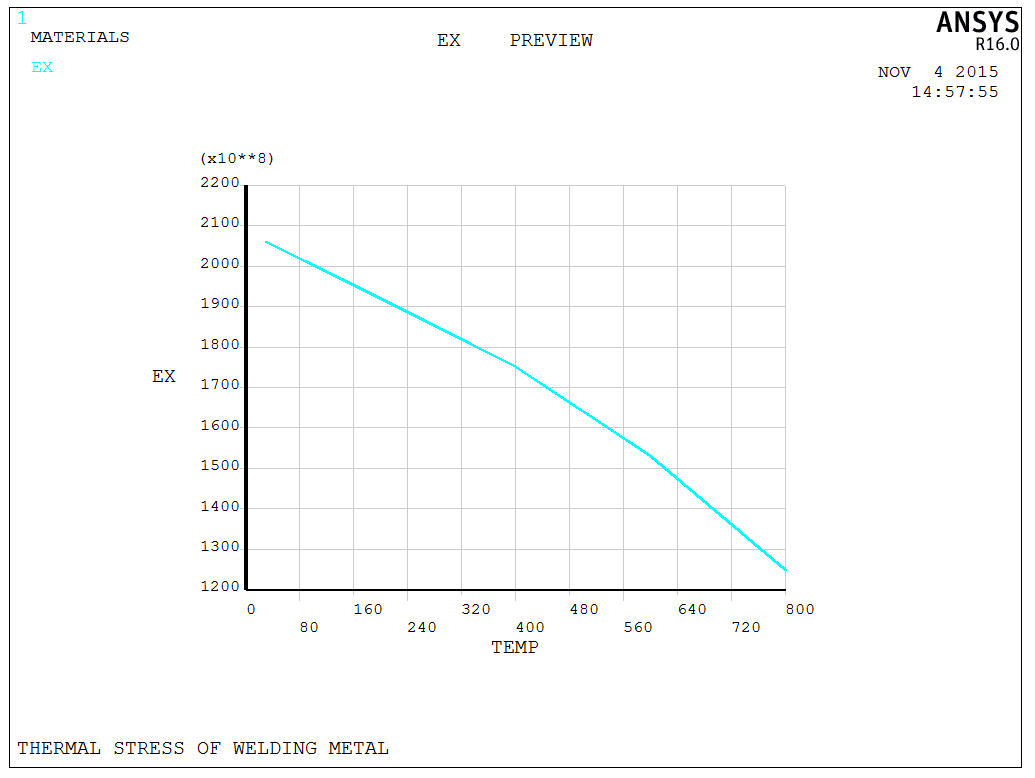
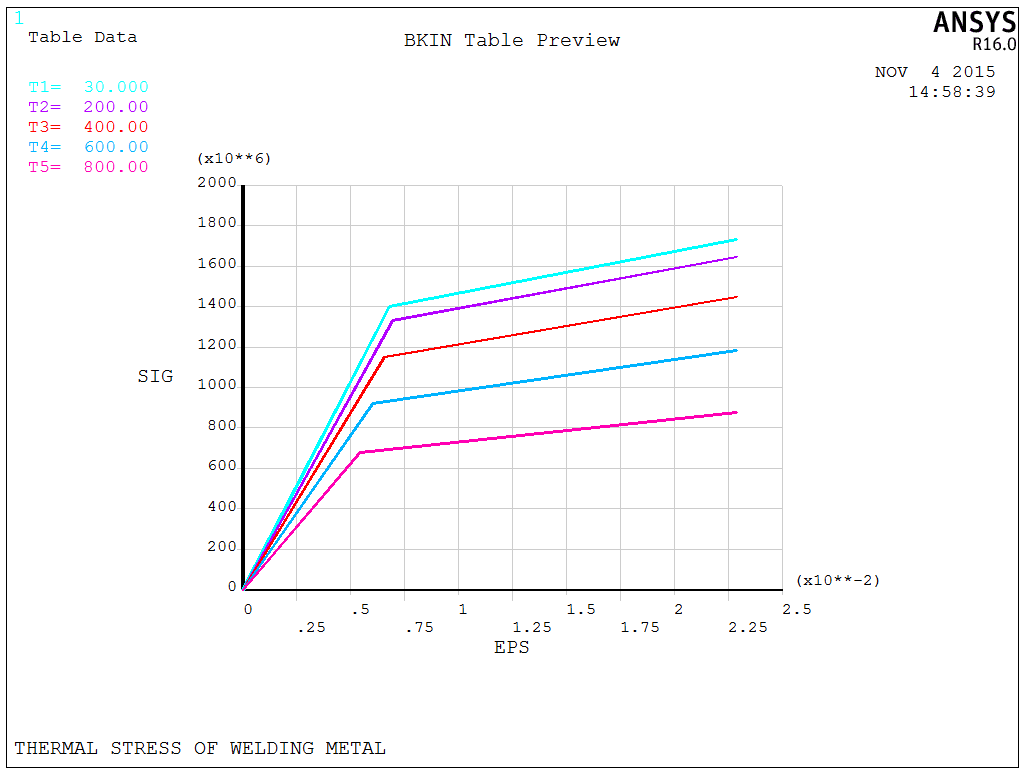
Since both the linear parameters (elastic modulus) and nonlinear parameters (yield strength, etc.) of the materials are temperature-dependent, it is necessary to set multiple temperatures for them. In APDL, MPDATA can be used to set linear parameters, while TBDATA can be used to set the relationship between nonlinear parameters and temperature. After setting the parameters, we can build the model.
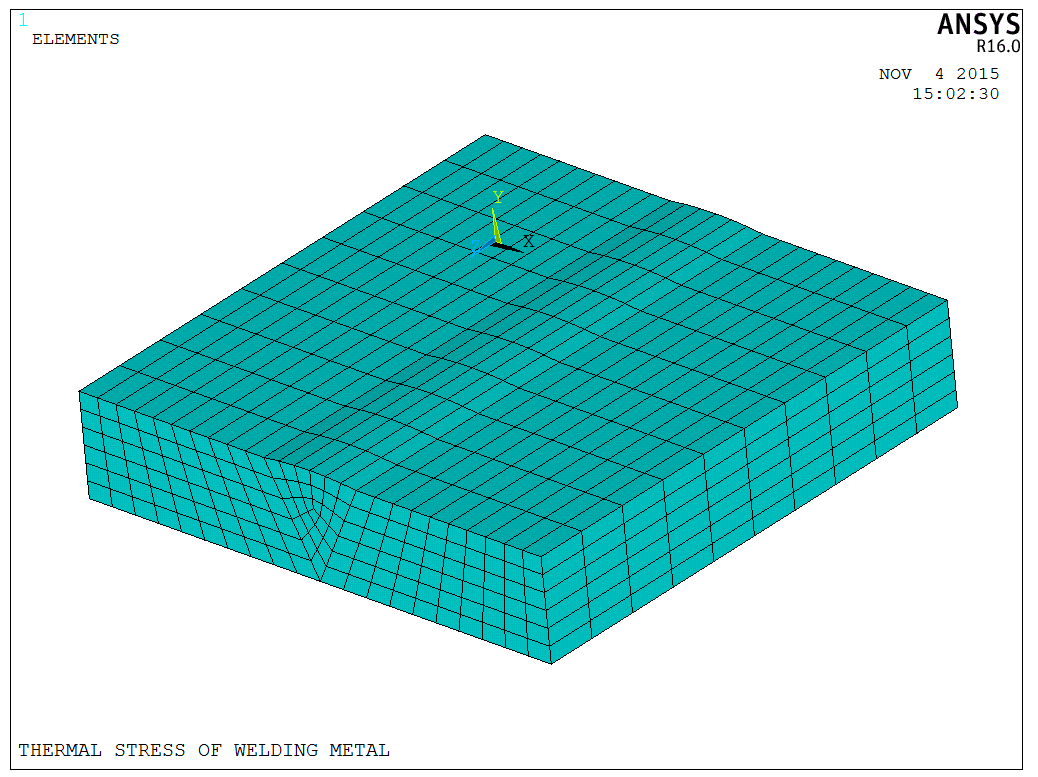
The model is relatively straightforward. Based on the dimensions, first use AREA to create the plane and divide the mesh. Then we can use VOFFST for volume extrusion to extrude the final finite element model. It is important to set the finite element size with ESIZE before extrusion, here the model is divided into 10 sections.
Based on the problem, transient analysis is used, mainly considering the time integration of structure and temperature. Open the time integration controls,
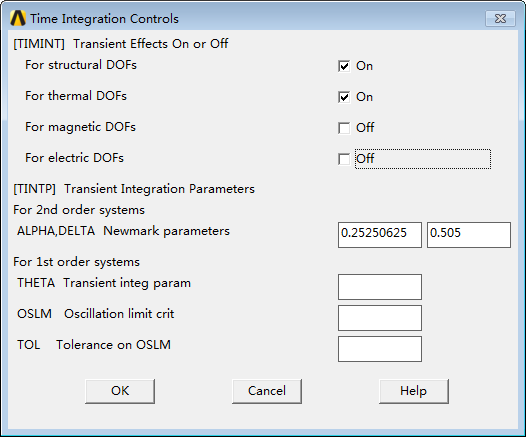
Then, set the time to 600s and enter the loading step.
Based on the temperature requirements, first set the overall temperature to 800 degrees using the TUNIF command or define the thermodynamic load in the GUI. After setting, set the convection as follows:
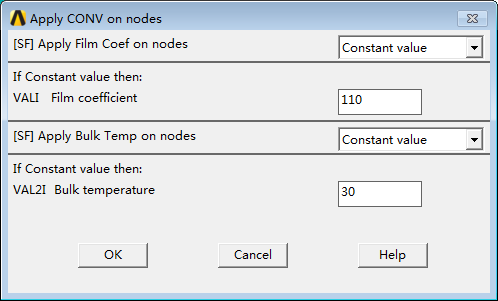
After applying the load, be sure to select the entire model before solving.
Due to the simplicity of the model, the solution speed is fast, and the temperature field and displacement field of the model can be quickly determined, as shown in the following figures (Temperature field, stress in X direction, displacement in X direction):
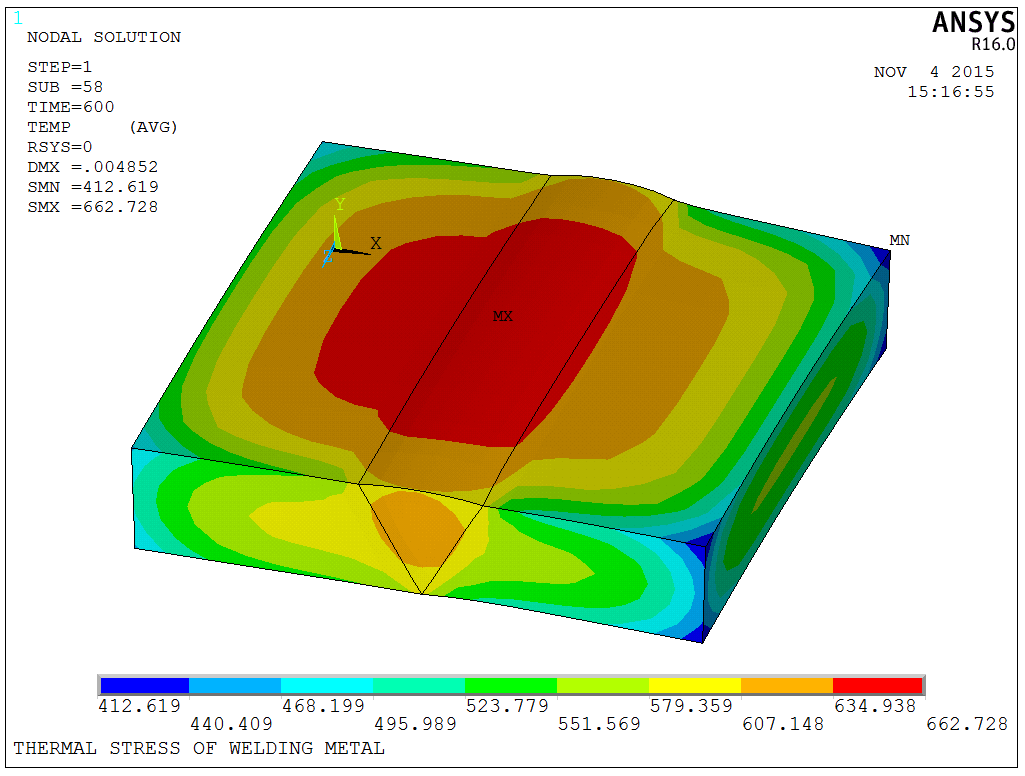
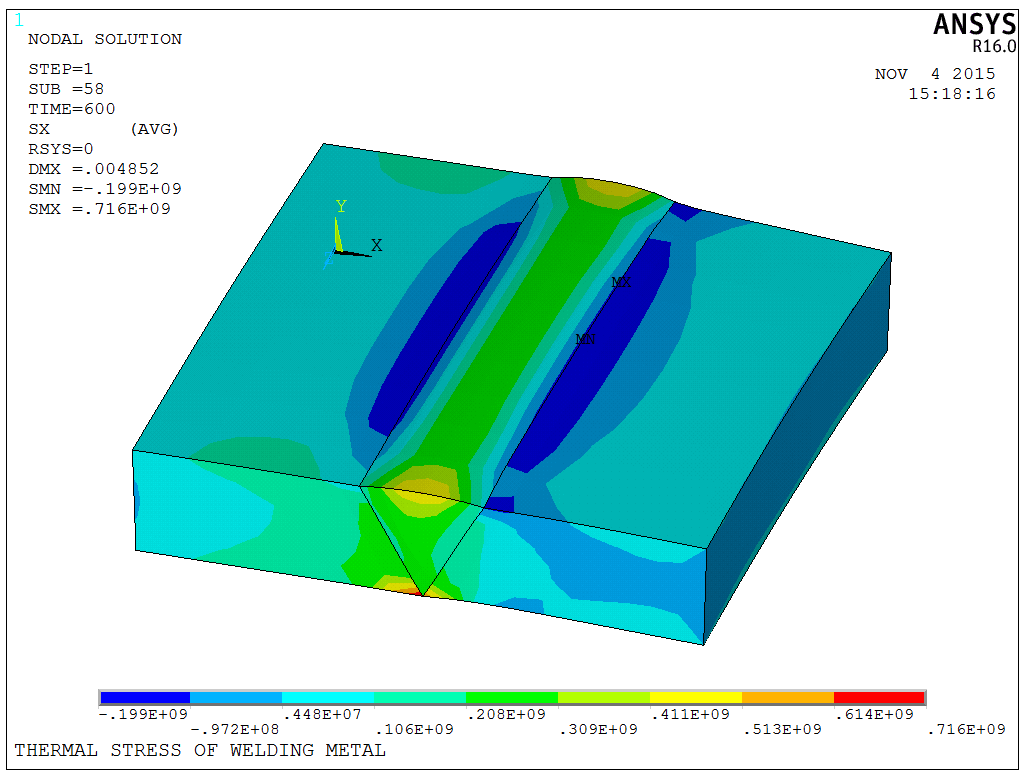
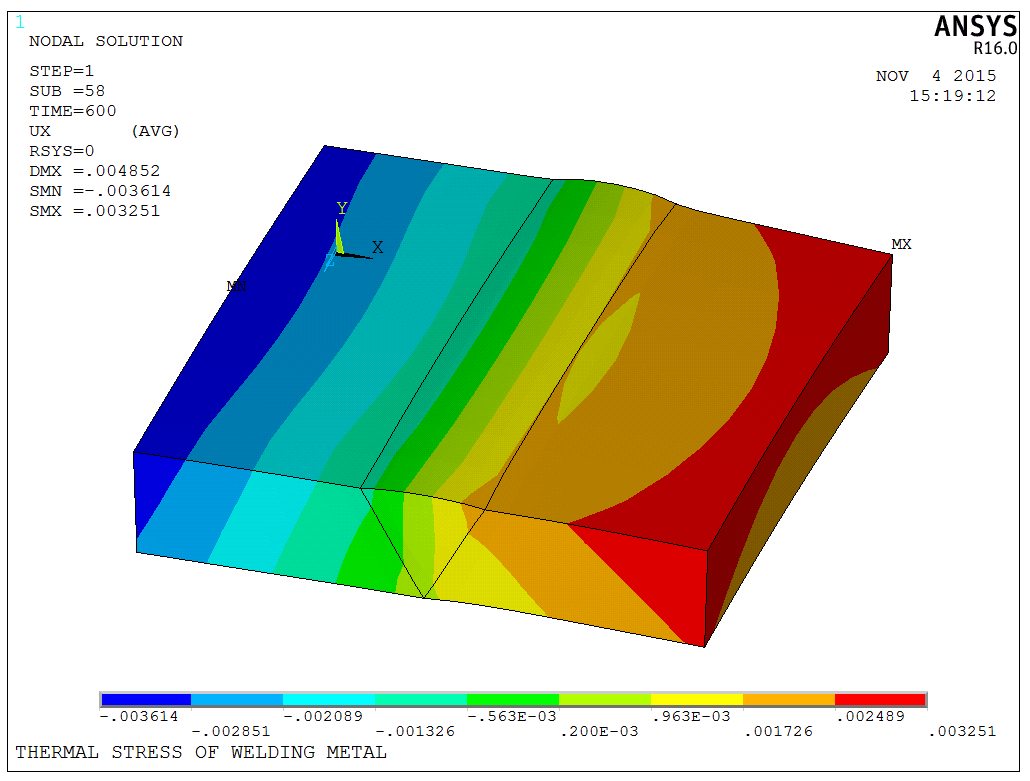
The model is a test model, and the APDL code is available upon request.